栈的基本概念
栈的定义
栈:是只允许在一端进行插入或删除的线性表。首先栈是一种线性表,但限定这种线性表只能在某一端进行插入和删除操作。
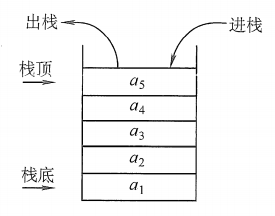
栈顶(Top):线性表允许进行插入删除的那一端。
栈底(Bottom):固定的,不允许进行插入和删除的另一端。
空栈:不含任何元素的空表。
栈又称为后进先出(Last In First Out)的线性表,简称LIFO结构
栈的常见基本操作
InitStack(&S):初始化一个空栈S
StackEmpty(S):判断一个栈是否为空,若栈为空则返回true,否则返回false
Push(&S, x):进栈(栈的插入操作),若栈S未满,则将x加入使之成为新栈顶
Pop(&S, &x):出栈(栈的删除操作),若栈S非空,则弹出栈顶元素,并用x返回
GetTop(S, &x):读栈顶元素,若栈S非空,则用x返回栈顶元素
DestroyStack(&S):栈销毁,并释放S占用的存储空间(“&”表示引用调用)
栈的顺序存储结构
栈的顺序存储
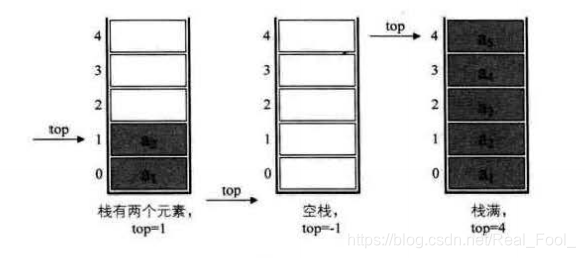
采用顺序存储的栈称为顺序栈,它利用一组地址连续的存储单元存放自栈底到栈顶的数据元素,同时附设一个指针(top)指示当前栈顶元素的位置。
若存储栈的长度为MAXSIZE,则栈顶位置top必须小于MAXSIZE。当栈存在一个元素时,top等于0,因此通常把空栈的判断条件定位top等于-1。
栈的顺序存储结构可描述为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| #define MAXSIZE 5
typedef struct SqStack{
int data[MAXSIZE];
int top;
}SqStack;
|
若现在有一个栈,MAXSIZE是5,则栈的普通情况、空栈、满栈的情况分别如下图所示:
初始化
1
2
3
4
5
| void InitStack(SqStack* S){
S->top = -1;
}
|
为什么要用 S->top = -1?
顺序栈的本质是一个数组,栈顶指针 top 表示当前栈顶元素在数组中的位置索引。
初始化时 top = -1 有
空栈条件:top == -1
当栈中没有元素时,top 指向数组的“前一个位置”(即无效索引),逻辑上表示“无元素”。
入栈操作
先让 top++,移动到下一个可用位置;将新元素存入 data[top]。
例如,第一次入栈时,top 从 -1 变为 0,元素存入 data[0],对应数组的第一个索引。
判断栈满
栈满条件:top == MAX_SIZE - 1
如果数组大小为 MAX_SIZE,当 top 指向最后一个位置(即 MAX_SIZE - 1)时,表示栈已满。
判断栈空
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| bool StackEmpty(SqStack* S){
if( S->top == -1){
return true;
}
return false;
}
|
进栈
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| bool Push(SqStack* S, int x){
if( S->top == MAXSIZE - 1 ){
return false;
}
S->top++ ;
S->data[S->top] = x;
return true;
}
|
出栈
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| bool Pop(SqStack* S, int* x) {
if (StackEmpty(S)) {
printf("栈空,无法出栈\n");
return false;
}
*x = S->data[S->top];
S->top--;
printf("出栈元素: %d\n", *x);
return x;
}
|
读栈顶元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| bool GetTop(SqStack* S, int* x) {
if (StackEmpty(S)) {
printf("栈空,无栈顶元素\n");
return false;
}
*x = S->data[S->top];
printf("当前栈顶元素: %d\n", *x);
return true;
}
|
出栈和读栈顶元素操作需要返回两个信息:
- 是否成功(通过
bool 返回值)。
- 得到的元素值(通过
int* x 指针参数)。
完整代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAXSIZE 5
typedef struct SqStack {
int data[MAXSIZE];
int top;
} SqStack;
void InitStack(SqStack* S) {
S->top = -1;
}
bool StackEmpty(SqStack* S) {
return (S->top == -1);
}
bool StackFull(SqStack* S) {
return (S->top == MAXSIZE - 1);
}
bool Push(SqStack* S, int x) {
if (StackFull(S)) {
printf("栈已满,无法入栈 %d\n", x);
return false;
}
S->top++;
S->data[S->top] = x;
printf("入栈元素: %d\n", x);
return true;
}
bool Pop(SqStack* S, int* x) {
if (StackEmpty(S)) {
printf("栈空,无法出栈\n");
return false;
}
*x = S->data[S->top];
S->top--;
printf("出栈元素: %d\n", *x);
return x;
}
bool GetTop(SqStack* S, int* x) {
if (StackEmpty(S)) {
printf("栈空,无栈顶元素\n");
return false;
}
*x = S->data[S->top];
printf("当前栈顶元素: %d\n", *x);
return true;
}
void PrintStack(SqStack* S) {
if (StackEmpty(S)) {
printf("栈空\n");
return;
}
printf("栈内容 (从底到顶): ");
for (int i = 0; i <= S->top; i++) {
printf("%d ", S->data[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
SqStack S;
int val;
InitStack(&S);
PrintStack(&S);
Push(&S, 10);
Push(&S, 20);
Push(&S, 30);
Push(&S, 40);
Push(&S, 50);
Push(&S, 60);
PrintStack(&S);
GetTop(&S, &val);
Pop(&S, &val);
Pop(&S, &val);
PrintStack(&S);
Pop(&S, &val);
Pop(&S, &val);
Pop(&S, &val);
Pop(&S, &val);
PrintStack(&S);
return 0;
}
|
栈的链式存储结构
采用链式存储的栈称为链栈,链栈的优点是便于多个栈共享存储空间和提高其效率,且不存在栈满上溢的情况。通常采用单链表实现,并规定所有操作都是在单链表的表头进行的。这里规定链栈没有头节点,Lhead指向栈顶元素
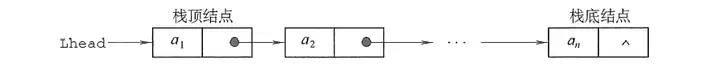
对于空栈来说,链表原定义是头指针指向空,那么链栈的空其实就是top=NULL的时候。
链栈的结构定义:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
typedef struct LinkedStackNode
{
int data;
struct LinkedStackNode * next;
} LinkedStackNode, * LinkedStack;
LinkedStack top;
|
初始化空栈
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
LinkedStack Init_LinkedStack()
{
LinkedStack top=(LinkedStackNode * )malloc (sizeof( LinkedStackNode));
if(top!=NULL)
top->next=NULL;
return top;
}
|
判断栈空
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
int LinkedStack_Empty(LinkedStack top)
{
if(top->next==NULL)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
|
入栈
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| int Push_LinkedStack(LinkedStack top,elemtype x)
{
LinkedStackNode * node;
node=(LinkedStackNode * )malloc(sizeof(LinkedStackNode));
if(node==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
node->data=x;
node->next=top->next;
top->next=node;
return 1;
}
}
|
出栈
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| int Pop_LinkedStack(LinkedStack top, elemtype *x)
{ LinkedStackNode * node;
if(top->next==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
node=top->next;
*x=node->data;
top->next=node->next;
free (node);
return 1;
}
}
|
取栈顶元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| int GetTop_LinkedStack(LinkedStack top)
{
if(top->next)
{
return top->next->data;
}
return -1;
}
|
求栈长
设置计数器,随top指针后移,计数器加1,直到遍历完所有元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
int Length_LinkedStack(LinkedStack top)
{
int count = 0;
while(top->next!=NULL)
{
++count;
top=top->next;
}
return count;
}
|
完整代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct LinkedStackNode
{
int data;
struct LinkedStackNode * next;
} LinkedStackNode, * LinkedStack;
LinkedStack top;
LinkedStack Init_LinkedStack()
{
LinkedStack top=(LinkedStackNode * )malloc (sizeof( LinkedStackNode));
if(top!=NULL)
top->next=NULL;
return top;
}
int LinkedStack_Empty(LinkedStack top)
{
if(top->next==NULL)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
int Push_LinkedStack(LinkedStack top,elemtype x)
{
LinkedStackNode * node;
node=(LinkedStackNode * )malloc(sizeof(LinkedStackNode));
if(node==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
node->data=x;
node->next=top->next;
top->next=node;
return 1;
}
}
int Length_LinkedStack(LinkedStack top)
{
int count = 0;
while(top->next!=NULL)
{
++count;
top=top->next;
}
return count;
}
int Pop_LinkedStack(LinkedStack top, elemtype *x)
{ LinkedStackNode * node;
if(top->next==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
node=top->next;
*x=node->data;
top->next=node->next;
free (node);
return 1;
}
}
int GetTop_LinkedStack(LinkedStack top)
{
if(top->next)
{
return top->next->data;
}
return -1;
}
void main()
{
int i,t,x,a[20];
LinkedStack top=Init_LinkedStack();
x=LinkedStack_Empty(top);
if(x=0)
{
printf("栈为空\n");
}
printf("请依次输入5个数,开始入栈:\n");
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
Push_LinkedStack(top,a[i]);
x=GetTop_LinkedStack(top);
if(x!=-1)
{
printf("当前栈顶元素为%d\n",x);
}
}
printf("入栈结束\n");
printf("栈长为%d\n",Length_LinkedStack(top));
printf("开始出栈:\n");
for (i=0;i<5;i++)
{
Pop_LinkedStack(top,&t);
printf("%d",t);
}
printf("\n");
printf("出栈后栈长为%d\n",Length_LinkedStack(top));
}
|


